Quantitative tumor stem cell analysis is a very complex investigation and, to our knowledge, can currently only be performed in clinical routine in one laboratory worldwide ind Germany. In the following, we will discuss the significance and possible applications.
What are stem cells?
Cancer stem cells are probably the most dangerous cells in a tumor, as they can divide indefinitely and transform into different tumor cells and have the ability to colonize tissues and form metastases. In many cases, they are also more resistant to a wide variety of drugs than circulating tumor cells (CTCs), which consist primarily of “dormant,” inactive cells. Tumor stem cells account for from 0 to approximately 12% of circulating tumor cells, depending on the aggressiveness of the tumor.
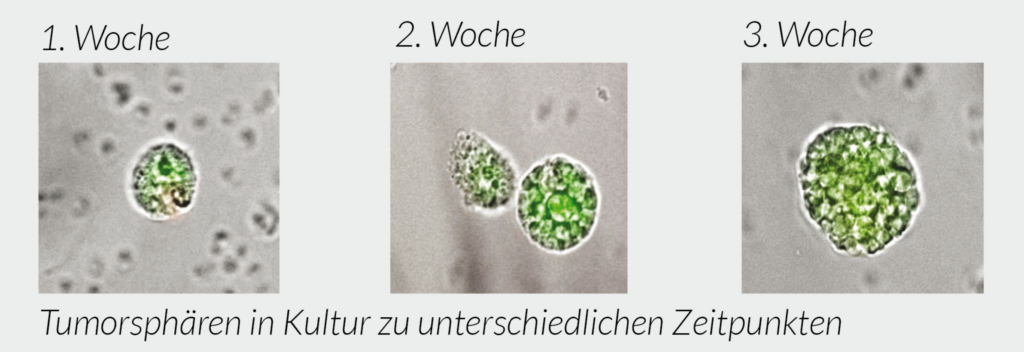
Tumor spheroids in culture at week 1, week 2 and at week 3.
What is a stemtrac® – tumor stem cell analysis?
stemtrac® is an innovative blood test that can detect the presence and activity of cancer stem cells in the blood of cancer patients. With stemtrac® , both tumor cells with stem cell characteristics can be found in the blood and active agents can be tested for their efficacy against these stem cells. This can enable individual risk assessment and therapy optimization.
How to identify tumor stem cells?
The stemtrac® test is based on the in vitro cultivation of blood samples from cancer patients. Within approximately 2 weeks, spherical structures (30-100µm) known as tumor spheres are formed in a special medium. They consist of a mother cell and can contain up to 100 daughter cells, each of which already has a new mutation. The tumor spheres exhibit characteristics typical of cancer stem cells, such as the ability to self-renew, expression of stem cell markers, and resistance to many chemotherapeutic agents.
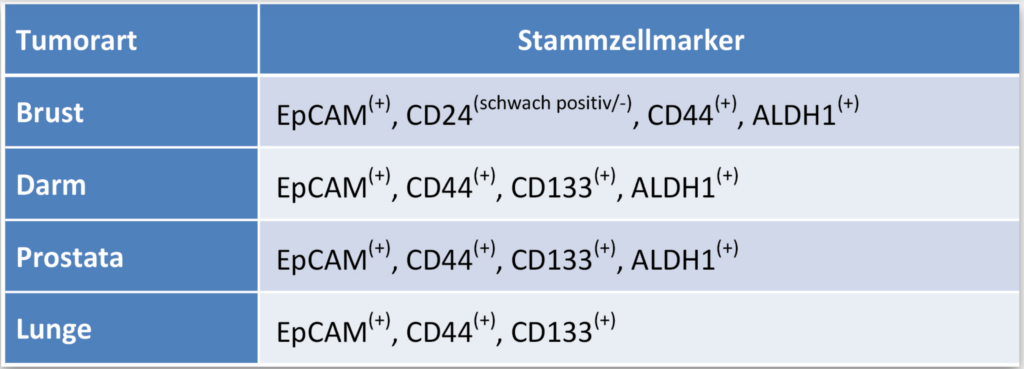
Different tumor cell types and their specific surface markers
Significance of stem cells and their medical relevance
The number of tumor spheroids found correlates significantly with the tumor stage in breast cancer. The more spheroids, the more aggressive the tumor. So far, no tumor spheres have been cultured in the blood of healthy volunteers.
Why and when to perform a stem cell analysis?
A stemtrac®-test is particular useful, when
- there is an increase in tumor cells circulating in the blood again after tumor clearance,
- in a metastasized situation
- in a metastatic situation, without therapy, the number of CTCs in the blood suddenly drops steeply,
- in the metastatic situation, no EpCAM
Analysis result received – What now?
The more tumor spheres found in a tumor stem cell analysis, the more aggressive the tumor – and the higher the risk of metastasis! If more than 300 tumor spheres per milliliter of blood are detected in patients, it is recommended to use further imaging procedures to detect possible metastases.
Therapy optimization with stemtrac®
Therapy optimization with stemtrac® is based on drug testing on tumor spheres grown from living circulating tumor stem cells. These measurements are not yet routinely established and are currently under evaluation. Different drugs or combinations of drugs are applied to the tumor spheres and their survival rate is measured. The goal of tumor therapy should not only be to focus on circulating tumor cells (maintrac®), but absolutely also on circulating tumor stem cells. As shown in the following picture, tumor spheroids are often more resistant to typical chemotherapeutic agents.
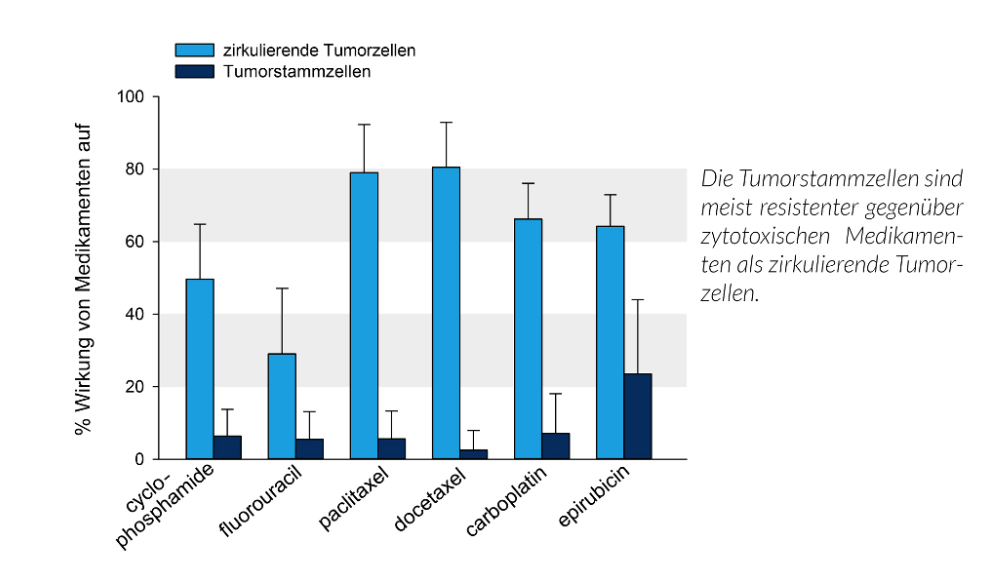
Light blue CTCs vs dark blue stem cells and the efficacy on both types with different drug. stem cells are usually more resistant against cytotoxic agents.
As soon as we have fully evaluated this method, we will inform you about our regular professional information, just sign up for the list below!
Literature:
- Pizon, M. et al. Heterogeneity of circulating epithelial tumour cells from individual patients with respect to expression profiles and clonal growth (sphere formation) in breast cancer. ecancer medicalscience 2013, 7:343 10.3332/ecancer.2013.343 (2013)
- Pizon, M. et al. The number of tumorspheres cultured from peripheral blood is a predictor for presence of metastasis in patients with breast cancer. Oncotarget, Advance Publications 2016, 10.18632/oncotarget.10174 (2016)
